Bronchitis: Understanding Cough and How to Manage It
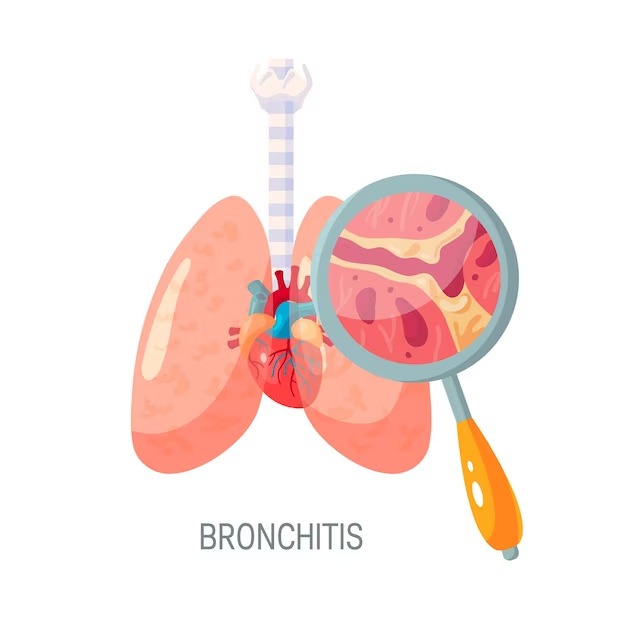
Bronchitis is a common respiratory condition that causes inflammation in the large airways (bronchi) of your lungs. This inflammation in bronchi leads to production of excess mucus, which can make breathing difficult and trigger a cough.
What are Bronchi and How Do They Get Inflamed?
The bronchi are the first division of your windpipe (trachea) dividing into the right and left lung. They further branch out into smaller tubes called segmental bronchi and subsegmental bronchi finally to smaller bronchioles eventually reaching the tiny air sacs (alveoli) where oxygen exchange occurs. In a normal individual, the walls of the bronchi produce mucus in small amount to trap dust, pollen, and other irritants that could otherwise damage your lungs.
During a viral or bacterial infection, or when an allergen, or irritant like smoke enters the airways, they can lead to inflammation(swelling) in the bronchi. This inflamed state triggers the production of excessive mucus, leading to narrowing of the breathing tubes thus making it harder to breathe and prompting the body to expel the mucus through coughing.
Causes of Bronchitis
Bronchitis can be caused by various factors, although viral infections are the most common culprit. Let’s explore the different causes:
Viral Infections: Viruses responsible for the common cold or flu often trigger bronchitis. These viruses spread through airborne droplets expelled when someone coughs or sneezes, or by touching contaminated surfaces.
Bacterial Infections: While less frequent than viral bronchitis and more commonly as secondary to a viral infection, bacterial infections can also cause bronchitis.
Irritants: Inhaling pollutants like smog, pollutants, dust, chemical exposure, or tobacco smoke can irritate the bronchi and lead to bronchitis. Occupational exposure to irritants like grain dust, textiles, ammonia, or strong acids can also trigger bronchitis.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Bronchitis
The persisting symptom of bronchitis is cough. You might experience other symptoms similar to a cold or flu, such as:
- Sore throat
- Headache
- Runny or blocked nose
- Body aches and pains
- Fatigue
In some cases, shortness of breath or wheezing may occur because of airway narrowing caused by inflammation and excessive mucous production. However, these symptoms are more common with chronic bronchitis, a long-term condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of acute bronchitis resolve on their own with home remedies, it’s crucial to seek medical attention from a pulmonologist or chest physician if you experience ANY OF THE ABOVE symptoms:
- A severe cough lasting more than two weeks
- A high fever (above 100.4°F) for more than three days
- Coughing up blood-streaked mucus
- Rapid breathing (more than 30 breaths per minute)
- Chest pain
- Drowsiness or confusion
- Recurrent similar episodes
Additionally, if you have underlying health conditions like asthma, heart failure, emphysema, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or chronic liver disease, consult your chest physician even with mild symptoms of bronchitis.
At Kalyan Hospital, we offer a comprehensive approach to diagnose and manage pulmonary diseases like pneumonia, bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung diseases(lung fibrosis), tuberculosis and lung cancer.